DDCMS智能合约设计与实现
DDCMS智能合约设计与实现
# DDCMS智能合约设计与实现
# DDCMS智能合约概述
DDCMS使用基于Solidity的智能合约进行开发。Solidity的智能合约语义上是图灵完备的,该语言支持各种基础类型(Booleans,Integers,Address,Bytes,Enum等)、复杂类型(Struct,Mapping,Array等)、复杂的表达式、控制结构和远程调用,以及接口、继承等面向对象的高级语言特性。Solidity是以太坊和FISCO-BCOS所支持的智能合约语言。
智能合约功能强大,因而真实世界中的复杂商业逻辑和应用可以在区块链上轻松实现。然而,智能合约一旦部署,它会在所有区块链节点上独立重复运行,因此原则上认为,只有各业务方需要进行共识的、逻辑可复用的业务才有必要通过智能合约在链上实现。此外,智能合约发布之后,若出现问题需要修复或者业务逻辑变更,是无法通过简单地在原有合约基础上修改再重新发布来解决的。因此,在设计之初还需要结合业务场景思考合适的合约更新机制。总体上,DDCMS合约的设计原则是:功能完备、逻辑清晰、模块解耦、结构清晰、安全完备、支持升级。
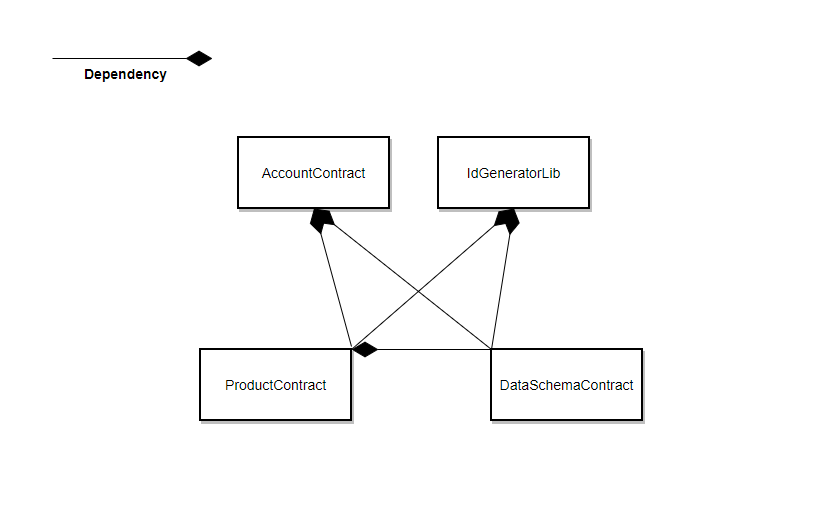
DDCMS-Contract用于追踪DDCMS的使用过程,数据目录生命周期中的每一个关键环节均会在链上留痕、存证,保证系统的可追溯、可监管。 它由三个模块构成:AccountContract, ProductContract, DataSchemaContract,由系统运营方部署。
AccountContract: 负责账户管理,包括机构的注册、审核等功能。系统中的数据提供方、见证机构,均需要在AccountContract中注册并审核,才能使用DDCMS。系统运营方则会在部署合约时自动注册。ProductContract: 负责业务管理,包括业务的创建、审核等功能。其中,业务的创建由数据提供方进行,其审核由见证方进行,当票数超过半数,即通过审核。DataSchemaContract:负责数据目录管理,包括数据目录的创建、审核等。其中,数据目录的创建由数据提供方进行,其审核由见证方进行,当票数超过半数,即通过审核。
下文将会基于业务目标对这三个模块展开描述。
# AccountContract智能合约
# 概述
AccountContract合约的主要目的是提供一个基本的账户管理机制,使用户可以在区块链上注册账户,并由管理员审核和管理账户。通过使用合约中定义的账户类型和状态,可以根据需求限制不同账户的权限和功能。这种账户管理机制可以用于各种场景,例如身份验证、权限控制和数据访问控制等。
# 角色与权限
不同角色(Person、Company、Witness、Admin)拥有不同的操作权限:
| 操作 | Person | Company | Witness | Admin |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 审核用户操作 | N | N | Y | Y |
| 增删业务、数据目录管理 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
| 审核业务、数据目录管理 | N | N | Y | Y |
| 查询业务操作 | Y | Y | Y | Y |
# 存储结构
存储结构主要包映射(mapping)和结构体(struct):
addressToDid:这是一个地址(address)到 DID 的映射。它用于快速查找已注册账户的 DID。通过将用户的地址与其对应的 DID 关联起来,可以方便地根据地址查询账户信息。didToAccount:这是一个 DID 到账户数据的映射。它存储了所有已注册账户的数据。使用 DID 作为键值,可以根据 DID 快速定位到相应的账户数据,而无需遍历整个映射。AccountData结构体:该结构体定义了账户数据的格式。它包含以下字段:address:账户的地址。did:账户的 DID。accountType:账户的类型。accountStatus:账户的状态。hash:账户的哈希值。
在DDCMS的分布式数据管理中,DID(Decentralized Identifier)作为身份标识符具有以下好处和优势:
- 去中心化身份验证:DID是一个去中心化的身份标识符,它不依赖于中心化的身份验证机构或第三方服务商。每个参与者都可以拥有自己的DID,并通过私钥对其进行控制和验证,从而实现去中心化的身份验证过程。
- 数据隐私保护:使用DID作为身份标识符的好处之一是可以更好地保护个人数据的隐私。在DDCMS中,账户数据可以通过DID进行访问和共享,而无需直接暴露个人身份信息。这样可以减少敏感数据泄露的风险,增加数据隐私的保护性。
- 可验证性和可信度:DID结合了公钥密码学,确保了DID持有者的身份可验证且不可伪造。DID的公钥可以用于验证数字签名,从而确保数据的完整性和真实性。这使得其他参与者可以相信所使用的DID的身份,从而增加了系统的可信度。
- 无需第三方信任:使用DID作为身份标识符可以消除对第三方的信任需求。每个参与者都可以独立验证和控制自己的DID,而无需依赖中心化的身份验证机构。这种去中心化的信任模式提供了更大程度的自主权和安全性。
- 跨系统互操作性:DID是一种开放、标准化的身份标识符,在不同的系统和平台之间具有互操作性。当DDCMS与其他分布式系统或应用集成时,使用DID可以方便地跨系统地识别和关联账户数据,实现数据的无缝交互和共享。
- 弹性和扩展性:DID的设计允许灵活地扩展和管理身份标识符。在DDCMS中,可以根据需要添加新的DID类型、属性或验证方法,以适应不同的身份需求和场景。这使得系统具有更强的弹性和可扩展性。
使用DID作为身份标识符可以为DDCMS带来以下好处:
- 提供可信、去中心化的身份验证机制。
- 加强个人数据的隐私保护。
- 增加系统的安全性和防护能力。
- 降低依赖第三方的信任需求。
- 实现分布式系统的互操作性和数据共享。
# 接口说明
register接口(用户注册)
- 用户调用此函数来注册一个账户,参数
accountType表示账户类型,hash是需要提供的哈希值。函数会检查参数的有效性,并且确保地址没有重复注册。注册成功后,会生成唯一的标识符(DID),并将账户信息存储在映射中,并触发AccountRegisteredEvent事件。
approve接口(审核用户)
- 管理员调用此函数来审核账户。参数
did是待审核账户的标识符,agree表示是否同意审核。检查账户是否存在和审核状态是否正确。审核通过后,更新账户状态为已审核,并根据账户类型增加统计数量,并触发AccountApprovedEvent事件。审核不通过则更新账户状态为已拒绝,并触发AccountDeniedEvent事件。
getAccountByDid接口(根据标识符查询账户信息)
- 根据标识符查询账户的详细信息,并返回
AccountData结构体。
getAccountByAddress接口(根据地址查询账户信息)
- 根据地址查询账户的详细信息,并返回
AccountData结构体。
pragma solidity >=0.6.0 <=0.8.17;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
// 账户合约
contract AccountContract {
// 账户注册事件
event AccountRegisteredEvent(
bytes32 did, // 账户的唯一ID
address addr, // 账户地址
AccountType accountType, // 账户类型
bytes32 hash //
);
// 账户批准事件
event AccountApprovedEvent(bytes32 did);
// 账户拒绝事件
event AccountDeniedEvent(bytes32 did);
//枚举类型和结构体定义
enum AccountType {
Person, //个人 (0 预留)
Company, //公司 (1)
Witness, //数据见证方 (2)
Admin //管理员 (3)
}
// 审核的状态枚举变量
enum AccountStatus {
Approving, //审核中 (0)
Approved, //已审核 (1)
Denied, //已拒绝 (2)
Disabled //禁用 (3 预留)
}
// 账户的数据
struct AccountData {
address addr; //账户地址
bytes32 did; //唯一标识符
AccountType accountType; //账户类型
AccountStatus accountStatus;//账户状态
bytes32 hash; //哈希值
}
// 存储
mapping(address => bytes32) public addressToDid; // 地址到 DID 的映射,用于快速查找注册的账户
mapping(bytes32 => AccountData) public didToAccount; // DID 到账户数据的映射,存储了所有已注册的账户
mapping(AccountType => uint256) public accountTypeNumbers; // 不同账户类型数量的统计
// 修饰符 判断只有管理员权限
modifier onlyAdmin() {
AccountData memory accountData = _getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
require(
accountData.accountStatus == AccountStatus.Approved,
"Invalid account status"
);
require(
accountData.accountType == AccountType.Admin,
"Account are not admin"
);
_;
}
// 构造函数
constructor() public{
_register(
msg.sender,
AccountType.Admin,
AccountStatus.Approved,
bytes32(0)
);
}
// 用户函数(注册账户)
function register(
AccountType accountType,
bytes32 hash
) external returns (bytes32 did) {
// 检查参数
require(hash != bytes32(0), "Invalid hash");
address addr = msg.sender;
require(addressToDid[addr] == bytes32(0), "address already registered");
// 注册账户
did = _register(addr, accountType, AccountStatus.Approving, hash);
}
// 管理员函数(审核账户)
function approve(bytes32 did, bool agree) external onlyAdmin {
// 获取账户信息
AccountData storage account = didToAccount[did];
require(account.addr != address(0), "Account not exist");
require(
account.accountStatus == AccountStatus.Approving,
"Invalid account status"
);
// 根据审核结果,更新账户状态和账户类型数量
if (agree) {
account.accountStatus = AccountStatus.Approved;
accountTypeNumbers[account.accountType]++;
emit AccountApprovedEvent(did);
} else {
account.accountStatus = AccountStatus.Denied;
emit AccountDeniedEvent(did);
}
}
// 根据唯一ID查询账户信息
function getAccountByDid(
bytes32 did
) external view returns (AccountData memory) {
return didToAccount[did];
}
// 根据地址查询账户信息
function getAccountByAddress(
address addr
) external view returns (AccountData memory) {
return _getAccountByAddress(addr);
}
// 生成唯一ID标识符
function _generateDid(
AccountType userType,
address initAddr,
bytes32 hash
) internal pure returns (bytes32 id) {
uint256 header = uint256(userType) << 240;
uint256 body = (uint256(keccak256(abi.encodePacked(initAddr, hash))) <<
16) >> 16;
id = bytes32(header | body);
}
// 注册账户
function _register(
address accountAddress,
AccountType accountType,
AccountStatus accountStatus,
bytes32 hash
) internal returns (bytes32 did) {
did = _generateDid(accountType, accountAddress, hash);
addressToDid[accountAddress] = did;
didToAccount[did] = AccountData(
accountAddress,
did,
accountType,
accountStatus,
hash
);
emit AccountRegisteredEvent(did, accountAddress, accountType, hash);
}
// 根据地址查询账户信息
function _getAccountByAddress(
address addr
) internal view returns (AccountData memory) {
bytes32 did = addressToDid[addr];
require(did != 0, "address not registered");
return didToAccount[did];
}
}
# ProductContract智能合约
# 概述
ProductContract合约的业务逻辑是管理业务的创建和审批过程,并记录相关的投票信息。
该合约导入了AccountContract合约,具有用户账户的权限管理,主要包含四个核心函数,分别是createProduct、approveProduct、getProduct和getVoteInfo。createProduct函数允许公司账户创建新的业务,要求提供有效唯一的业务散列值,创建业务完成触发事件该业务进行上链。approveProduct函数由见证人账户调用,用于审批所有的业务,根据投票结果超过半数,将该业务状态变为已批准或已拒绝,触发业务投票事件。getProduct函数用于查询业务的详细信息,包括散列值、所有者ID和状态。最后,getVoteInfo函数用于查询业务的投票信息,包括同意的数量、反对数量、通过阈值和见证人数量。
在我们的分布式数据管理(DDCMS)智能合约中,可以实现去中心化、不可篡改的文档存储,提高透明度和可追溯性,自动化任务通过智能合约,实现更安全的身份验证和访问控制,减少中介成本,跨边界合作,确保数据隐私。这种整合为文档管理系统带来了更高的效率、可信度和可扩展性,促进了数据安全和合规性。
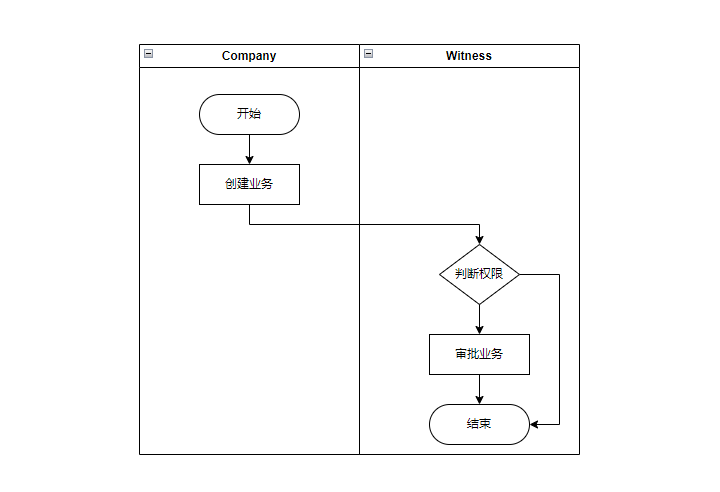
# 业务流程图
有两个角色权限,分别是Company和Witness。Company可以新增业务,然后Witness作为见证人可以对该业务进行审批。
# 存储结构
ProductInfo 结构体:用于存储业务产品的基本信息,包括哈希值、所有者ID和业务状态。这个结构体的设计允许合约跟踪每个产品的状态和所有者。
VoteInfo 结构体:用于存储有关业务产品投票的信息,包括同意票数、否决票数、投票阈值和见证人数量。这个结构体的设计有助于确保业务产品是否被批准或否决,并根据见证人的数量来动态计算阈值。
mapping 数据结构:用于维护多个映射,包括:
products:将业务产品ID与ProductInfo结构体相关联,以便按ID检索产品信息。hashToId:将业务产品哈希与产品ID相关联,以确保每个产品具有唯一的哈希值。ownerProductCount:跟踪每个所有者创建的产品数量,用于生成唯一的产品ID。productCreationVotes:将产品ID与VoteInfo结构体相关联,用于管理产品的投票信息。productVoters:将产品ID与见证人的投票状态相关联,以确保每个见证人只能投一票。
优势和好处:
- 数据不可篡改性: 区块链的核心特性之一是数据的不可篡改性。每个业务产品的信息都被写入区块链,一旦写入,就无法修改或删除。这确保了业务产品的文档和元数据的完整性和安全性,防止数据被恶意篡改或删除。
- 透明度和可追溯性: 区块链上的数据是公开可查的,任何人都可以查看业务产品的状态、审批历史和投票结果。这增加了透明度,所有操作都可以被追溯,有助于防止不当行为和提高信任。
- 自动化审批和投票: 合约允许自动化审批和投票过程,减少了中介的需要。这加快了审批流程,降低了操作风险,减少了人为错误的可能性。
- 去中心化: DDCMS采用去中心化的设计,没有单点故障,无需信任任何中央机构或第三方。这提高了系统的可用性和鲁棒性。
- 权限控制: 通过修饰符实现了严格的权限控制,确保只有具有正确权限的账户可以执行特定操作。这有助于防止未经授权的访问和操作。
- 可扩展性: 存储结构允许添加新的产品和见证人,而不需要对合约进行大规模的修改。这使得系统具有良好的可扩展性,能够适应不断增长的文档管理需求。
# 接口说明
createProduct接口(创建一个新的业务)
- 创建一个新的业务,并将其添加到合约中。在创建业务之前,如确保哈希值有效且不重复。然后生成一个唯一的业务标识符ID,并将产品信息存储到映射表中。同时,根据已注册的见证人数量初始化投票参数,然后触发
CreateProductEvent事件。
approveProduct接口(见证人对业务进行审批)
- 对业务标识符和状态进行验证,确保产品存在且处于审批中的状态。然后根据见证人的投票意见更新同意票数、否决票数,并根据投票结果判断是否通过审批。如果同意票数达到阈值,则业务状态更新为已通过,否则如果否决票数超过一半以上,则业务状态更新为已否决。最后,更新见证人的投票记录,并触发
VoteProductEvent事件。
getProduct接口(查询业务的详细信息)
- 根据业务标识符从映射表中获取产品信息,并对业务的存在性进行验证。返回该业务的详细信息,包括哈希值、所有者ID和状态。
getVoteInfo接口(查询业务投票信息)
- 根据业务标识符从映射表中获取投票信息,返回同意票数、否决票数、投票阈值和见证人数量。
pragma solidity >=0.6.0 <=0.8.17;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import "./IdGeneratorLib.sol";
import "./AccountContract.sol";
// 业务管理合约
contract ProductContract {
// 创建业务事件
event CreateProductEvent(bytes32 productId, bytes32 hash);
// 投票当前的业务产品事件
event VoteProductEvent(
bytes32 productId,
bytes32 voterId,
bool agree,
uint256 agreeCount,
uint256 denyCount,
ProductStatus afterStatus
);
// 枚举类型定义业务的状态
enum ProductStatus {
Approving, // 审批中
Approved, // 已通过
Denied, // 已否决
Disabled, // 已禁用
Banned // 已封禁
}
// 存储业务的结构体
struct ProductInfo {
bytes32 hash; // 哈希值
bytes32 ownerId; // 所有者ID
ProductStatus status; // 业务状态
}
// 存储投票信息的结构体
struct VoteInfo {
uint256 agreeCount; // 赞同票数
uint256 denyCount; // 否决票数
uint256 threshold; // 投票阈值
uint256 witnessCount; // 见证人数量
}
// 账户合约
AccountContract private accountContract;
// 存储产品信息的映射
mapping(bytes32 => ProductInfo) products;
// 维护产品归属关系的映射
mapping(bytes32 => bytes32) private hashToId;
// 存储产品创建投票信息的映射
mapping(bytes32 => uint256) private ownerProductCount;
// 限定只有公司账户可以调用的修饰符
mapping(bytes32 => VoteInfo) private productCreationVotes;
// 限定只有见证人账户可以调用的修饰符
mapping(bytes32 => mapping(bytes32 => bool)) public productVoters;
// 限定只有公司账户可以调用的修饰符
modifier onlyCompany() {
_requireAccount(msg.sender, AccountContract.AccountType.Company);
_;
}
// 限定只有见证人账户可以调用的修饰符
modifier onlyWitness() {
_requireAccount(msg.sender, AccountContract.AccountType.Witness);
_;
}
// 构造函数,初始化与账户合约的地址
constructor(address _accountContract) public {
accountContract = AccountContract(_accountContract);
}
//创建业务的函数
function createProduct(
bytes32 hash
) external onlyCompany returns (bytes32 productId, uint256 witnessCount) {
//requires
require(hash != bytes32(0), "Invalid hash");
require(hashToId[hash] == 0, "duplicate product hash");
//Generate product id
AccountContract.AccountData memory owner = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
uint256 ownerNonce = ownerProductCount[owner.did];
productId = IdGeneratorLib.generateId(owner.did, ownerNonce);
products[productId] = ProductInfo(
hash,
owner.did,
ProductStatus.Approving
);
hashToId[hash] = productId;
ownerNonce++;
ownerProductCount[owner.did] = ownerNonce;
//Initialize voting params
witnessCount = accountContract.accountTypeNumbers(
AccountContract.AccountType.Witness
);
productCreationVotes[productId] = VoteInfo(
0,
0,
witnessCount / 2 + 1,
witnessCount
);
emit CreateProductEvent(productId, hash);
}
// 可见机构审批业务
function approveProduct(
bytes32 productId,
bool agree
)
external
onlyWitness
returns (
bytes32 witnessDid,
uint256 agreeCount,
uint256 denyCount,
ProductStatus afterStatus
)
{
//Product id validation
ProductInfo storage product = products[productId];
require(product.ownerId != bytes32(0), "product not existed");
require(
product.status == ProductStatus.Approving,
"Invalid product status"
);
VoteInfo storage voteInfo = productCreationVotes[productId];
//Vote
AccountContract.AccountData memory witness = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
witnessDid = witness.did;
require(!productVoters[productId][witnessDid], "Duplicate vote");
uint256 threshold = voteInfo.threshold;
if (agree) {
agreeCount = voteInfo.agreeCount + 1;
voteInfo.agreeCount = agreeCount;
denyCount = voteInfo.denyCount;
if (agreeCount >= threshold) {
afterStatus = ProductStatus.Approved;
}
} else {
denyCount = voteInfo.denyCount + 1;
voteInfo.denyCount = denyCount;
agreeCount = voteInfo.agreeCount;
if (denyCount > (voteInfo.witnessCount - 1) / 2) {
afterStatus = ProductStatus.Denied;
}
}
product.status = afterStatus;
productVoters[productId][witnessDid] = true;
//event
emit VoteProductEvent(
productId,
witnessDid,
agree,
agreeCount,
denyCount,
afterStatus
);
}
// 查询业务详细信息
function getProduct(
bytes32 productId
) external view returns (ProductInfo memory productInfo) {
productInfo = products[productId];
require(productInfo.ownerId != 0, "Product not exist");
}
// 查询投票人信息
function getVoteInfo(
bytes32 productId
) external view returns (VoteInfo memory) {
return productCreationVotes[productId];
}
// 判断当前的账户是否状态正常
function _requireAccount(
address addr,
AccountContract.AccountType accountType
) internal view {
AccountContract.AccountData memory accountInfo = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(addr);
require(
accountInfo.accountStatus == AccountContract.AccountStatus.Approved,
"Invalid account status"
);
require(
accountInfo.accountType == accountType,
"Account is not witness"
);
}
}
# DataSchemaContract智能合约
# 概述
DataSchemaContract合约是一个数据目录管理合约,主要业务是创建和管理业务产品的数据目录。数据目录管理是指用于描述和定义数据结构的模板或规范,它定义了产品中的各种数据字段、类型和关联规则等信息。该合约是导入了AccountContract合约和ProductContract合约,是基于用户权限管理和业务产品的管理上开发的。
用户创建和审批数据目录管理。用户可以提供数据模式的哈希值和所属业务产品的ID,创建后处于审核中状态。见证人可以投票同意或反对,根据投票门槛来确定审批结果。用户可以查询数据模式信息和投票详情。这个合约确保了数据目录管理的安全。
用户可以查询数据目录管理共享的详细信息和投票情况。这提供了透明度和可追溯性,用户可以了解数据模式的来源和状态,以及投票结果的信息。这符合DDCMS的开放和透明的原则,用户可以参与到数据目录的管理和决策过程中。
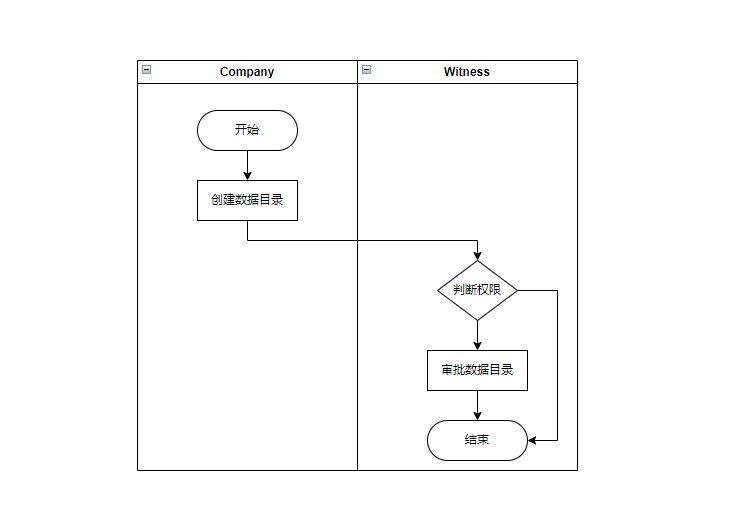
# 业务流程图
这里也是有两个角色权限,分别是Company和Witness。Company可以新增数据目录管理,然后Witness作为见证人可以对该数据目录进行审批。
# 存储结构
DataSchemaInfo 结构体:用于存储数据目录管理的信息,包括数据模式的哈希值(hash)、拥有者的ID(ownerId)、业务的ID(productId)以及数据目录的状态(status)。这个结构体用于追踪每个数据目录管理的基本信息。
VoteInfo 结构体:用于存储数据目录管理创建时的投票信息,包括同意数(agreeCount)、反对数(denyCount)、投票门槛(threshold)以及见证者数量(witnessCount)。这个结构体用于追踪数据目录管理的投票情况。
mapping 数据结构:合约中使用了多个 mapping 数据结构来存储关键信息:
dataSchemas:通过数据目录管理ID查找数据模式信息。hashToId:通过数据目录管理哈希值查找数据目录管理ID。productDataSchemaCount:记录每个业务的数据目录管理数量,用于生成唯一的数据目录管理ID。dataSchemaCreationVotes:存储数据目录管理创建的投票信息,用于记录见证人的投票情况。dataSchemaVoters:存储数据目录管理的投票者,以防止重复投票。
优势和好处:
- **数据安全和完整性:**合约中的数据模式信息和投票信息存储在区块链的不可篡改的区块中,确保了数据的安全和完整性。任何对数据的修改都会被记录下来,并且可以通过区块链的共识算法来保证数据的一致性和真实性,提高数据的可信度。
- **透明度和追溯性:**由于存储结构设计使得数据模式信息和投票信息对所有参与者都是可见的,建立了一个透明和可追溯的数据管理系统。用户可以查看特定数据模式的详细信息和投票情况,确保了数据管理过程的公正性和可信度。
- **去中心化的决策机制:**通过见证人的投票机制,该合约为DDCMS提供了一个去中心化的决策机制。参与者可以根据自己的判断和利益,选择同意或反对数据模式的审批。这种去中心化的决策机制增加了系统的灵活性和民主性,避免了单一实体的控制和操纵。
它是去中心化的,意味着没有一个中心服务器掌控所有数据,而是分散存储在区块链网络中。其次,它具有可扩展性,可以轻松地添加更多的节点和参与者,使系统更加强大。此外,存储在区块链上的数据安全可靠,不能被篡改,确保了数据的安全性和完整性。所有参与者都可以查看数据模式的详细信息和投票情况,让系统变得更加透明和可追溯。这个存储结构让DDCMS成为一个开放、安全、可信的内容管理系统,能够满足各种需求,保证数据的质量和一致性。
# 接口说明
createDataSchema接口(创建数据目录)
- 该函数接受两个参数,数据目录的哈希值(
hash)和业务产品的ID(productId),返回数据模式的ID(dataSchemaId)和见证人数量(witnessCount)。在创建数据模式前,会进行参数校验,验证产品和拥有者的信息,并生成数据模式ID。
approveDataSchema接口(审批数据目录)
- 该函数接受两个参数,数据目录的ID(
dataSchemaId)和是否同意审批(agree),返回见证人的DID(witnessDid)、同意数(agreeCount)、反对数(denyCount)和审批后的数据模式状态(afterStatus)。只有见证人可以调用该函数。在审批数据模式前,会校验数据模式的状态,并进行投票,如果同意数达到门槛则通过,如果反对数超过一半则拒绝。
getDataSchema接口(获取数据模式信息)
- 该函数接受数据目录的ID作为参数,返回数据目录的详细信息,包括哈希值、拥有者ID、产品ID和数据目录状态。
getVoteInfo接口(获取投票信息)
- 该函数接受数据目录的ID作为参数,返回数据目录创建的投票信息,包括同意数、反对数、投票门槛和见证人数量。
pragma solidity >=0.6.0 <=0.8.17;
pragma experimental ABIEncoderV2;
import "./IdGeneratorLib.sol";
import "./AccountContract.sol";
import "./ProductContract.sol";
// 数据目录管理业务合约
contract DataSchemaContract {
// 创建数据目录管理事件
event CreateDataSchemaEvent(bytes32 dataSchemaId, bytes32 hash);
// 见证人审批数据目录管理事件
event VoteDataSchemaEvent(
bytes32 dataSchemaId,
bytes32 voterId,
bool agree,
uint256 agreeCount,
uint256 denyCount,
DataSchemaStatus afterStatus
);
// 枚举类型定义数据目录管理的状态
enum DataSchemaStatus {
Approving, // 审核中
Approved, // 已审核通过
Denied, // 已拒绝
Disabled, // 已禁用
Banned // 已封禁
}
// 存储数据目录管理的信息
struct DataSchemaInfo {
bytes32 hash; // 数据模式的哈希值
bytes32 ownerId; // 拥有者的ID
bytes32 productId; // 业务的ID
DataSchemaStatus status; // 数据目录的状态
}
// 存储投票信息
struct VoteInfo {
uint256 agreeCount; // 同意数
uint256 denyCount; // 反对数
uint256 threshold; // 投票门槛,超过该门槛则通过
uint256 witnessCount; // 见证者数量
}
// 账户合约实例
AccountContract private accountContract;
// 业务合约实例
ProductContract private productContract;
// 存储数据目录管理的映射,通数据目录管理ID查找数据模式信息
mapping(bytes32 => DataSchemaInfo) dataSchemas;
// 存储数据目录管理哈希值到数据目录管理ID的映射
mapping(bytes32 => bytes32) private hashToId;
// 存储产品的数据目录管理式数量
mapping(bytes32 => uint256) private productDataSchemaCount;
// 存储数据目录管理创建的投票信息
mapping(bytes32 => VoteInfo) private dataSchemaCreationVotes;
// 存储数据目录管理的投票者
mapping(bytes32 => mapping(bytes32 => bool)) private dataSchemaVoters;
//初始化构造函数 传入账户合约地址和业务合约地址
constructor(address _accountContract, address _productContract) public {
accountContract = AccountContract(_accountContract);
productContract = ProductContract(_productContract);
}
//只有见证人有权限
modifier onlyWitness() {
AccountContract.AccountData memory accountInfo = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
require(
accountInfo.accountStatus == AccountContract.AccountStatus.Approved,
"Invalid account status"
);
require(
accountInfo.accountType == AccountContract.AccountType.Witness,
"Account is not witness"
);
_;
}
// 创建数据目录管理理函数
function createDataSchema(
bytes32 hash,
bytes32 productId
) external returns (bytes32 dataSchemaId, uint256 witnessCount) {
//requires
require(hash != bytes32(0), "Invalid hash");
require(productId != bytes32(0), "Invalid productId");
require(hashToId[hash] == 0, "duplicate data schema hash");
// 获取当前的账户信息
AccountContract.AccountData memory ownerAccount = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
// 获取当前的业务信息
ProductContract.ProductInfo memory productInfo = productContract
.getProduct(productId);
//Validate product and owner
require(
productInfo.status == ProductContract.ProductStatus.Approved,
"product not approved"
);
require(
productInfo.ownerId == ownerAccount.did,
"must be product owner"
);
require(
ownerAccount.accountStatus ==
AccountContract.AccountStatus.Approved,
"owner not approved"
);
// 生成数据目录管理ID
uint256 productNonce = productDataSchemaCount[productId];
dataSchemaId = IdGeneratorLib.generateId(productId, productNonce);
dataSchemas[dataSchemaId] = DataSchemaInfo(
hash,
ownerAccount.did,
productId,
DataSchemaStatus.Approving
);
hashToId[hash] = dataSchemaId;
productNonce++;
productDataSchemaCount[productId] = productNonce;
witnessCount = accountContract.accountTypeNumbers(
AccountContract.AccountType.Witness
);
dataSchemaCreationVotes[dataSchemaId] = VoteInfo(
0,
0,
witnessCount / 2 + 1,
witnessCount
);
emit CreateDataSchemaEvent(dataSchemaId, hash);
}
// 审核数据目录管理函数
function approveDataSchema(
bytes32 dataSchemaId,
bool agree
)
external
onlyWitness
returns (
bytes32 witnessDid,
uint256 agreeCount,
uint256 denyCount,
DataSchemaStatus afterStatus
)
{
//Arg validations
require(dataSchemaId != 0, "Invalid data schema id");
// 获取当前的数据目录管理的信息
DataSchemaInfo storage dataSchema = dataSchemas[dataSchemaId];
require(
dataSchema.status == DataSchemaStatus.Approving,
"Invalid data schema status"
);
// 获取当前见证人账户信息
AccountContract.AccountData memory witness = accountContract
.getAccountByAddress(msg.sender);
witnessDid = witness.did;
VoteInfo storage voteInfo = dataSchemaCreationVotes[dataSchemaId];
require(!dataSchemaVoters[dataSchemaId][witnessDid], "Duplicate vote");
uint256 threshold = voteInfo.threshold;
uint256 witnessCount = voteInfo.witnessCount;
// 进行审批管理操作
if (agree) {
agreeCount = voteInfo.agreeCount + 1;
voteInfo.agreeCount = agreeCount;
denyCount = voteInfo.denyCount;
if (agreeCount >= threshold) {
afterStatus = DataSchemaStatus.Approved;
}
} else {
denyCount = voteInfo.denyCount + 1;
voteInfo.denyCount = denyCount;
agreeCount = voteInfo.agreeCount;
if (denyCount > (voteInfo.witnessCount - 1) / 2) {
afterStatus = DataSchemaStatus.Denied;
}
}
dataSchema.status = afterStatus;
dataSchemaVoters[dataSchemaId][witnessDid] = true;
emit VoteDataSchemaEvent(
dataSchemaId,
witnessDid,
agree,
agreeCount,
denyCount,
afterStatus
);
}
// 查询数据管理信息
function getDataSchema(
bytes32 dataSchemaId
) external view returns (DataSchemaInfo memory dataSchema) {
dataSchema = dataSchemas[dataSchemaId];
require(dataSchema.ownerId != 0, "data schema not exist");
}
// 查询投票人信息
function getVoteInfo(
bytes32 dataSchemaId
) external view returns (VoteInfo memory) {
return dataSchemaCreationVotes[dataSchemaId];
}
// 判断当前账户是否有权限
function _requireAccount(
address addr,
AccountContract.AccountType accountType
) internal view {}
}
# DDCMS智能合约依赖关系